CBDC’s
What are CBDC’s?
Central bank digital currencies, or CBDCs, are digital versions of a country’s fiat currency that are issued and regulated by the central bank. While CBDCs offer the potential for increased financial accessibility and efficiency, there are also concerns about the potential for government abuse of control.
By having direct control over a digital currency, governments would be able to monitor and track all financial transactions made by citizens, violating their privacy and civil liberties. The government would also have the power to freeze or seize individuals digital funds without proper legal justification, effectively giving them unchecked authority over people’s finances.
In addition, CBDCs could further concentrate power and wealth into the hands of the government and financial elites, leading to increased financial oppression for the general population. For example, the government could use its control over the currency to manipulate the economy and benefit large corporations, while ordinary citizens suffer the consequences of inflation and economic instability.
To avoid financial enslavement, it’s important to be aware of the potential drawbacks of CBDCs and to advocate for alternative financial systems like Bitcoin that prioritize privacy, freedom, and equality.
CBDCs won’t solve inflation as it’s a complex issue influenced by many factors.
Centralized control lead always to government manipulation and higher inflation.
To combat inflation, sound monetary policy like Bitcoin and a stable economy are crucial.
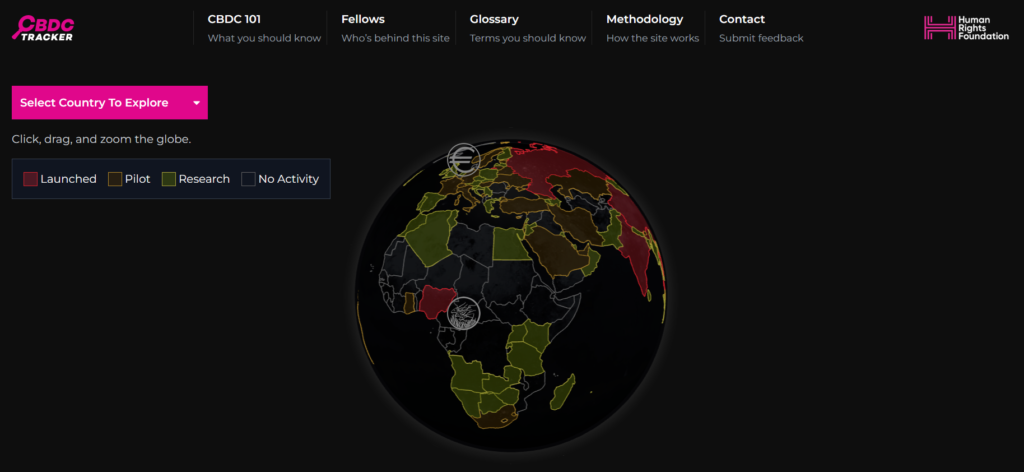
Here you can track the status of the CBDC by the country:

https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/cbdctracker/




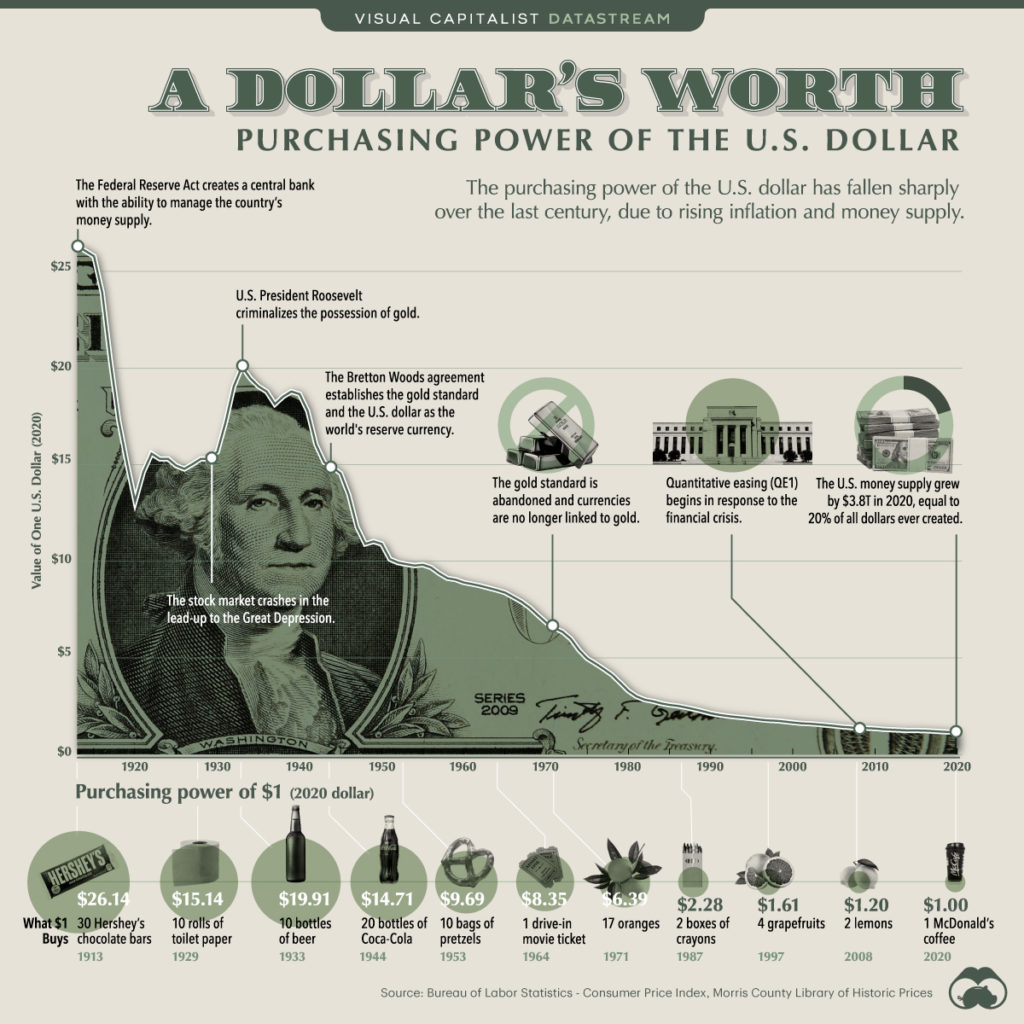
In 1971, the United States abandoned the gold standard and adopted a pure fiat currency system, meaning that the US dollar was no longer backed by gold. This event marked a significant change in the global monetary system and had far-reaching consequences for the international economy.
After the United States abandoned the gold standard in 1971, the value of the US dollar was no longer tied to a finite supply of gold. This gave the government more flexibility in controlling the money supply, but also created the risk of inflation.
The government could now simply print more money to pay for its expenses, which leads to an increase in the money supply and a decrease in the value of each individual dollar.
This process, known as money debasement, leads to inflation and erodes the purchasing power of people’s savings over time.
The use of a pure fiat currency system, such as the one adopted by the United States in 1971, has made it easier for governments to manipulate their currency and has led to the ongoing debasement of money.
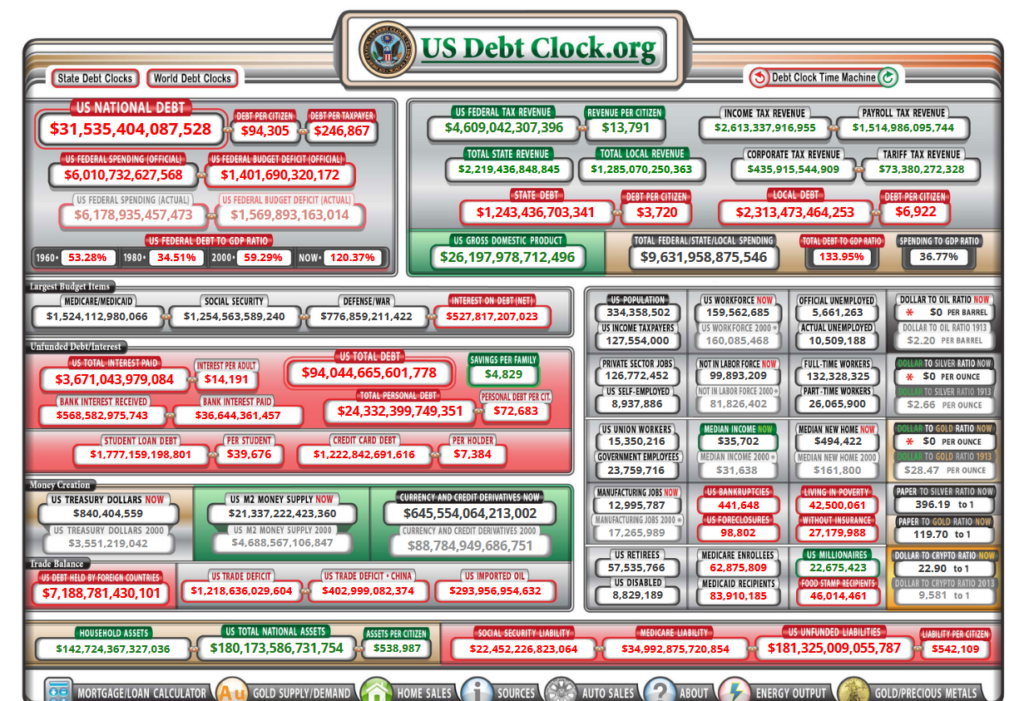
Fiat currency, or currency that is backed by a government and not by a tangible asset like gold or Bitcoin, has a failure rate of 100% because it is subject to inflation/hyperinflation and devaluation over time. The value of fiat currency decreases as more of it is printed (As of 2023, the United States national debt is estimated to be around $31.5 trillion) , causing prices to rise and purchasing power to decrease. This can lead to economic instability and the collapse of the currency.
The average life expectancy of fiat currencies is around 27 years, with some lasting longer and others failing much sooner. This is due to factors such as political instability, economic mismanagement, and high levels of debt.
Now ask yourself:
Why are we being forced by law, to use a money that is designed to lose value over time?